Translational research laboratory for advanced microbiology diagnosis and pathogen-host response in respiratory infections
Objectives
- To implement new and advanced diagnostic tools, specially focused on rapid diagnostic tools and imaging techniques for the microbial diagnosis of pneumonia and respiratory infections
- To study of respiratory microbiome unbalances during respiratory infections acquired in the community or in the nosocomial settings
- To study the role of biofilms in respiratory infections such as ventilator associated pneumonia or chronic respiratory infections (Cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis and Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases)
- To study the efficacy of new antibiotics and their pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) relationships to the aforementioned microorganisms
Projects in Progress
- Effect of Linezolid versus vancomycin in resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) biofilm within endotracheal tubes of patients admitted at the Respiratory Critical care Unit
- Association of P. aeruginosa biofilm with clinical on worse clinical prognosis in patients with non cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Effect of aerosolized antimicrobials in endotracheal tubes biofilm
- Validation of a new model of endotracheal tube biofilm caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Effect of monoclonal antibodies to prevent bacterial biofilm in endotracheal tubes
- Effect of corticosteroids in combination with antimicrobials to combat Streptococcus pneumoniae endotracheal biofilm
Milestones Achieved
- Validation studies for the use of microbiological rapid diagnosis through Unyvero-Curetis in Community Acquired pneumonia and Ventilator associated pneumonia
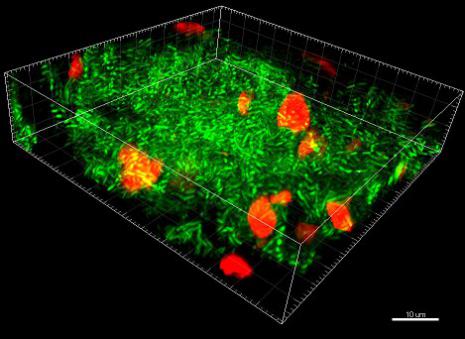
- Standardization of techniques for the study of biofilm within endotracheal tubes
- Standardization of inoculum preparation (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae) and microbial diagnosis in respiratory (EAT, BAL), blood samples and lung biopsies at autopsy for the all the pneumonia pig model experiments.
- Description of biofilm morphology within endotracheal tubes
- Assessment of the effect of systemic antimicrobials on endotracheal tubes biofilm from a pig model of MRSA pneumonia
- Effect of 2-week antipseudomona treatment on P. aeruginosa phenotypical shifts in Cystic Fibrosis patients
- Description of biofilm in patients with bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases chronically colonized with P. aeruginosa
Future Challenges
- Implementation rapid diagnostic tools and novel imaging techniques in the diagnostic of pneumonia and respiratory infections
- Understand the clinical importance of bacterial biofilm during nosocomial and chronic respiratory infections
- Descritpion of the effect of systemic antimicrobials on bacterial biofilm within endotracheal tubes
- Identification of new therapeutic targets to combat bacterial respiratory infections
- Describing respiratory microbiome unbalances during respiratory infections acquired in the community and in the nosocomial settings
Publications
Linezolid limits burden of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in biofilm of tracheal tubes.
Fernández-Barat L, Ferrer M, Sierra JM, Soy D, Guerrero L, Vila J, Li Bassi G, Cortadellas N, Martínez-Olondris P, Rigol M, Esperatti M, Luque N, Saucedo LM, Agustí C, Torres A.
Crit Care Med. 2012 Aug;40(8):2385-9.
Direct analysis of bacterial viability in endotracheal tube biofilm from a pig model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia following antimicrobial therapy.
Fernández-Barat L, Li Bassi G, Ferrer M, Bosch A, Calvo M, Vila J, Gabarrús A, Martínez-Olondris P, Rigol M, Esperatti M, Luque N, Torres A.
FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012 Jul;65(2):309-17
Diagnostic Value of Endotracheal Aspirates Sonication on Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Microbiologic Diagnosis.
Fernández-Barat L, Motos A, Ranzani OT, Bassi GL, Aguilera Xiol E, Senussi T, Travierso C, Chiurazzi C, Idone F, Muñoz L, Vila J, Ferrer M, Pelosi P, Blasi F, Antonelli M, Torres A.
Microorganisms. 2017 Sep 20;5(3). pii: E62. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms5030062.
Intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa with and without multidrug resistance.
Fernández-Barat L, Ferrer M, De Rosa F, Gabarrús A, Esperatti M, Terraneo S, Rinaudo M, Li Bassi G, Torres A.
J Infect. 2017 Feb;74(2):142-152.
Biofilms in ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Fernández-Barat L, Torres A
Future Microbiol. 2016 Dec;11:1599-1610. Epub 2016 Nov 10.
Phenotypic shift in Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations from cystic fibrosis lungs after 2-week antipseudomonal treatment.
Fernández-Barat L, Ciofu O, Kragh KN, Pressler T, Johansen U, Motos A, Torres A, Hoiby N.
J Cyst Fibros. 2017 Mar;16(2):222-229. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Sep 17.
Lines list
- Animal Model
- Bronchiectasis non associated to Cystic Fibrosis (BQ-noFQ), Cystic Fibrosis (CF) and immune deficiencies
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
- Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Networks, European Projects and Collaborations
- Noninvasive Ventilation (NIV)
- Pulmonary complications in immunocompromised (IC) patients
- Translational research laboratory for advanced microbiology diagnosis and pathogen-host response in respiratory infections
- Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)